Medical imaging reagents are specialized chemical or biological substances used to enhance the visibility, contrast, or specificity of anatomical structures, physiological processes, or pathological conditions during diagnostic imaging procedures. These reagents improve the diagnostic accuracy of modalities such as X-ray, computed tomography (CT), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), ultrasound, positron emission tomography (PET), single-photon emission computed tomography (SPECT), and optical imaging.
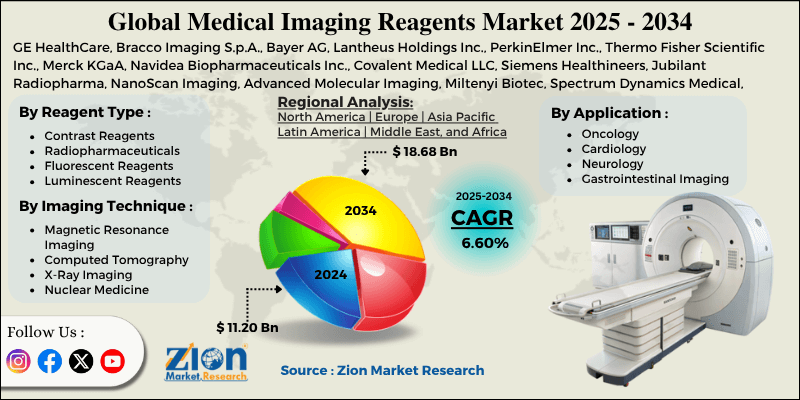
The concept of contrast agents dates back to the early 20th century with the use of barium sulfate for gastrointestinal X-rays and iodine compounds for angiography. Modern Medical Imaging reagents have evolved dramatically since the 1980s with the introduction of gadolinium-based MRI contrast agents, technetium-99m radiotracers for SPECT, and fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) for PET. As of 2025, the global medical imaging reagents market is valued at approximately USD 2.5–3 billion and is growing at a CAGR of 6–8%, driven by rising demand for early cancer detection, cardiovascular imaging, neurological disorders, and the rapid expansion of PET/CT and hybrid imaging systems worldwide. Major players include GE Healthcare, Bracco, Bayer (Gadavist), Lantheus Medical Imaging, Guerbet, and Siemens Healthineers.
These reagents transform diagnostic imaging from purely structural to functional and molecular, enabling clinicians to detect diseases at earlier stages and monitor treatment responses with greater precision.
Classification of Medical Imaging Reagents
Medical imaging reagents are classified by imaging modality, chemical nature, and clinical purpose:
- X-ray and Computed Tomography (CT) Contrast Agents Iodine-based compounds (ionic and non-ionic).
- Ionic: Diatrizoate, iothalamate.
- Non-ionic (preferred): Iohexol, iopamidol, iodixanol.
- Mechanism: High atomic number of iodine increases X-ray attenuation.
- Uses: Angiography, urography, gastrointestinal studies.
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) Contrast Agents Primarily gadolinium-based.
- Gadolinium chelates: Gadopentetate (Magnevist), gadoteridol (ProHance), gadobutrol (Gadavist), gadoxetate (Eovist).
- Mechanism: Shorten T1 relaxation time → bright enhancement on T1-weighted images.
- Uses: Brain tumors, liver lesions, vascular imaging.
- Non-gadolinium alternatives: Iron oxide nanoparticles (superparamagnetic), manganese-based.
- Ultrasound Contrast Agents Microbubbles filled with inert gas (perfluorocarbon, sulfur hexafluoride).
- Examples: SonoVue (sulfur hexafluoride microbubbles), Definity, Optison.
- Mechanism: Reflect ultrasound waves strongly → enhance echogenicity.
- Uses: Cardiac, liver, kidney perfusion imaging.
- Nuclear Medicine / PET & SPECT Reagents
- PET Tracers: Fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG-18F), PSMA-68Ga, amyloid tracers (florbetapir).
- SPECT Tracers: Technetium-99m (Tc-99m) for myocardial perfusion, bone scans.
- Mechanism: Radioactive decay detected by gamma camera or PET scanner.
- Optical Imaging Reagents Near-infrared dyes (indocyanine green, methylene blue).
- Uses: Sentinel lymph node mapping, intraoperative imaging.
Key Applications in Clinical Practice
- Oncology
- Contrast-enhanced CT/MRI for tumor staging.
- PET/CT with FDG for metabolic activity and metastasis detection.
- PSMA-targeted agents for prostate cancer.
- Neurology
- MRI with gadolinium for multiple sclerosis, brain tumors, stroke.
- Amyloid PET for Alzheimer’s diagnosis.
- Cardiology
- Myocardial perfusion imaging (SPECT/PET).
- Coronary CT angiography with iodine contrast.
- Gastrointestinal & Hepatobiliary
- Barium sulfate for GI tract.
- Hepatocyte-specific gadoxetate for liver lesion characterization.
- Musculoskeletal & Vascular
- MRI for soft tissue tumors, joint inflammation.
- CT angiography for vascular disease.
- Intraoperative & Interventional
- Indocyanine green for real-time visualization during surgery.
Safety Profile and Adverse Reactions
- Iodine-Based CT Contrast
- Risk: Contrast-induced nephropathy (CIN) in patients with renal impairment.
- Allergic reactions: Mild (hives) to severe anaphylaxis (rare).
- Prevention: Hydration, low-osmolar agents.
- Gadolinium-Based MRI Contrast
- Risk: Nephrogenic systemic fibrosis (NSF) in severe renal failure (now rare with newer agents).
- Gadolinium retention in brain (no proven clinical harm).
- Contraindication: eGFR <30 mL/min.
- Ultrasound Microbubbles
- Very safe; rare allergic reactions.
- Radiotracers
- Low radiation dose; short half-life (Tc-99m 6 hours, F-18 110 minutes).
Regulatory and Quality Standards
- FDA/EMA approval required for each contrast agent.
- Pharmacovigilance monitoring for rare reactions.
- Batch testing for purity and sterility.
Market and Major Products
| Modality | Leading Products | Manufacturer |
|---|---|---|
| CT Contrast | Omnipaque, Visipaque, Ultravist | GE, Bracco, Bayer |
| MRI Contrast | Gadavist, Dotarem, Clariscan | Bayer, Guerbet |
| Ultrasound | SonoVue, Definity, Optison | Bracco, Lantheus |
| PET Tracers | FDG, Amyvid, Axumin, PSMA-68Ga | Various |
Trends:
- Macrocyclic gadolinium (lower retention).
- Non-gadolinium MRI agents.
- Theranostic radiotracers (diagnosis + therapy).
Future Directions
- Targeted Agents: Tumor-specific probes (PSMA, HER2).
- Nanoparticle-Based: Multifunctional (imaging + therapy).
- AI-Enhanced Interpretation: Automated lesion detection.
- Low-Dose Radiotracers: Improved sensitivity.
- Portable Imaging: Miniaturized ultrasound contrast systems.
Conclusion
Medical imaging reagents are indispensable for accurate diagnosis, staging, treatment planning, and response monitoring in modern medicine. From iodine-based CT contrast to targeted PET tracers and gadolinium-enhanced MRI, these agents transform images from anatomical to functional and molecular, enabling precision medicine. Ongoing innovation focuses on safety (lower gadolinium retention), specificity (tumor-targeted), and sustainability (reduced radiation). As imaging modalities advance and AI integration deepens, medical imaging reagents will continue playing a pivotal role in early detection, personalized therapy, and improved patient outcomes across oncology, cardiology, neurology, and beyond.
More articles by ZMR Researche:
https://www.zionmarketresearch.com/de/report/interconnect-data-center-solution-market
https://www.zionmarketresearch.com/de/report/resolvers-market
https://www.zionmarketresearch.com/de/report/escape-room-market
https://www.zionmarketresearch.com/de/report/rx-medical-food-market
https://www.zionmarketresearch.com/de/report/immunochemistry-analyzers-market