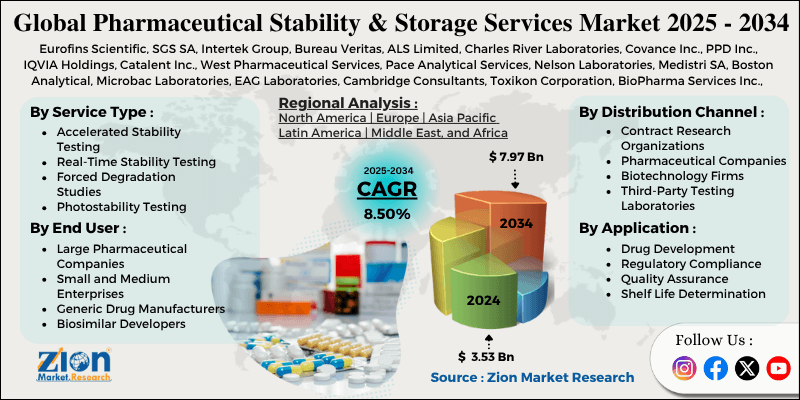
Pharmaceutical stability and storage services encompass specialized facilities, protocols, and testing programs designed to evaluate, maintain, and document the quality, safety, and efficacy of drug substances and products throughout their lifecycle. These services ensure compliance with international regulatory guidelines—primarily ICH (International Council for Harmonisation)—by simulating real-world and accelerated conditions to predict shelf life, identify degradation pathways, and establish appropriate storage conditions.
Stability testing originated in the mid-20th century as pharmaceutical quality standards evolved, becoming formalized with ICH Q1 guidelines in the 1990s. Today, outsourced stability and storage services form a critical segment of the Pharmaceutical Services Industry, valued at approximately USD 2-3 billion globally as of 2025, growing at 8-10% CAGR due to increasing biologic and complex generic development, globalization of supply chains, and stringent regulatory scrutiny. Leading providers include Catalent, SGS, Intertek, Thermo Fisher (Patheon), Eurofins, and Charles River, offering GMP-compliant chambers, analytical testing, and regulatory support.
These services are essential for product registration, commercial batch release, and post-market surveillance, preventing costly recalls and ensuring patient safety.
Importance of Stability Testing
Stability is defined as the capacity of a drug substance or product to remain within established specifications under specified storage conditions. Key objectives:
- Determine shelf life and expiry dating.
- Establish retest periods for APIs.
- Recommend storage conditions (e.g., “Store at 25°C” or “Refrigerated”).
- Identify degradation products and pathways.
- Validate packaging integrity.
Regulatory mandates:
- ICH Q1A-Q1F: Core stability guidelines.
- WHO, FDA, EMA, PMDA alignment.
- Required for IND, NDA, ANDA, BLA submissions.
Failure risks: Potency loss, impurity formation, microbial contamination, physical changes (dissolution, appearance).
Types of Stability Studies
- Long-Term (Real-Time) Intended storage conditions; defines shelf life.
- Intermediate For zones with climatic variability.
- Accelerated Elevated temperature/humidity to predict long-term behavior.
- Stress/Forced Degradation Extreme conditions (heat, light, pH, oxidation) to elucidate degradation pathways.
- Photostability (ICH Q1B) Light exposure (UV/visible).
- In-Use After opening/reconstitution.
- Freeze-Thaw For biologics.
- Registration vs. Follow-Up Pre-approval vs. post-market confirmatory.
ICH Stability Zones
Climatic zones guide conditions:
- Zone I/II (Temperate): 25°C/60% RH long-term.
- Zone III/IVa/IVb (Hot/Humid): 30°C/65-75% RH.
Storage Conditions and Facilities
GMP-compliant stability chambers:
- Temperature: -80°C to +60°C.
- Humidity: 5-95% RH.
- Photostability: ICH Q1B Option 1/2 (1.2 million lux-hours visible + 200 W·h/m² UV).
Features:
- Walk-in rooms, reach-in chambers.
- Redundant systems (backup power, alarms).
- 21 CFR Part 11 compliant monitoring (continuous data logging).
- Validated per IQ/OQ/PQ.
Specialized:
- Cryogenic (-80°C).
- High-humidity IVb.
- Custom (in-use, transport simulation).
Analytical Testing
Post-storage samples undergo:
- Assay/potency.
- Impurities/degradation products.
- Dissolution/disintegration.
- pH, appearance, particulate matter.
- Microbial limits.
- Water content.
Advanced: UPLC-MS, NMR for degradation elucidation.
Service Models
- Full-Service CROs Study design, chamber storage, testing, reporting.
- Storage-Only GMP chambers for sponsor-managed studies.
- Analytical-Only Testing of sponsor-stored samples.
- Consulting Protocol development, regulatory submission support.
Applications Across Product Types
- Small Molecules: Standard conditions.
- Biologics: Cold chain (2-8°C), freeze-thaw, agitation.
- Vaccines: Ultra-low temperature (-70°C).
- Generics: Bracketing/matrixing for reduced testing.
- Medical Devices/Combination Products: Unique requirements.
Benefits of Outsourcing
- Capital avoidance (chambers expensive).
- Expertise/compliance.
- Flexibility/scalability.
- Global reach (multi-zone storage).
Challenges
- Sample management/logistics.
- Cost (USD 100-500/sample/year).
- Capacity constraints (biologics boom).
- Data integrity (ALCOA+).
Trends
- Digitalization: Cloud-based LIMS, real-time monitoring.
- Sustainability: Energy-efficient chambers.
- Biologics focus (cold chain validation).
- Accelerated stability modeling (ASAPprime).
Regulatory Landscape
- ICH Q1A(R2): Stability testing new drug substances/products.
- Q1D: Bracketing/matrixing.
- Q1E: Evaluation for shelf life.
- Q5C: Biotechnological products.
- FDA/EMA: Strict GMP, data submission.
Conclusion
Pharmaceutical stability and storage services are indispensable for ensuring drug quality from development through commercialization. Advanced facilities, precise testing, and regulatory expertise enable accurate shelf-life determination and safe storage recommendations. As portfolios shift toward biologics and complex formulations, these services evolve with digital tools and sustainable practices. Outsourcing provides efficiency and compliance, supporting innovation while safeguarding patient health worldwide.
More articles by ZMR Researche:
https://www.zionmarketresearch.com/de/report/glycerol-monostearate-market
https://www.zionmarketresearch.com/de/report/anti-static-bags-for-electronics-market
https://www.zionmarketresearch.com/de/report/asset-recovery-services-market
https://www.zionmarketresearch.com/de/report/surface-mount-technology-market-size
https://www.zionmarketresearch.com/de/report/subsea-trencher-market