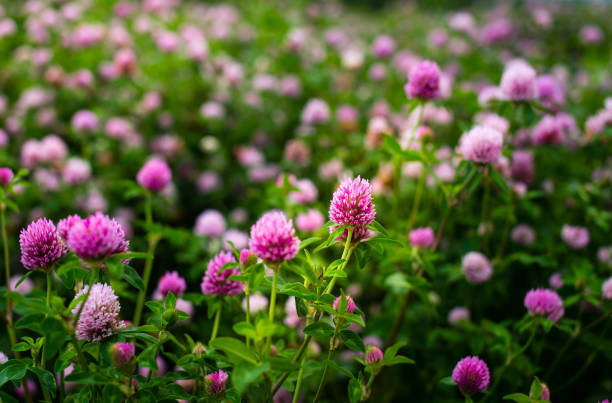
Red Clover (Trifolium pratense), also known as meadow clover or purple clover, is a perennial herbaceous legume native to Europe, Western Asia, and northwest Africa, now widely naturalized across temperate regions worldwide. Recognized for its vibrant pink-purple flower heads and trifoliate leaves, red clover has been valued for centuries in agriculture, traditional medicine, and ecology.
It serves as a high-protein forage crop, soil enhancer through nitrogen fixation, and source of bioactive compounds like isoflavones. In herbal medicine, red clover is popular for menopausal symptom relief and skin health, though scientific evidence varies.
Vibrant field of blooming red clover flowers.
Another view of red clover in full bloom across a meadow.
Extensive crimson clover field in agricultural landscape.

Botanical Description
Red clover is a short-lived perennial (typically 2-3 years) growing 20-80 cm tall, with erect or ascending stems. Its leaves are alternate and trifoliate, each leaflet oval-oblong (2-6 cm long) often marked with a pale V-shaped chevron.
The distinctive flower heads are dense, globular clusters of 50-100 pink to purple tubular florets, blooming from spring to autumn. Pollinated primarily by bees, it produces small kidney-shaped seeds.
Close-up of red clover’s trifoliate leaves.
Detailed view of young trifoliate leaves.
Botanical diagram illustrating red clover structure.
Cultivation and Agricultural Uses
Red clover thrives in well-drained, neutral to slightly acidic soils (pH 6-7) and cool, moist climates. It is sown as a cover crop, green manure, or forage, fixing 50-200 kg of nitrogen per hectare annually via symbiotic rhizobia bacteria.
In farming, it’s rotated with cereals to improve soil fertility, suppress weeds, and provide livestock feed (hay, silage, pasture). Varieties include medium red (diploid) and mammoth red (tetraploid, taller but less persistent).
Red clover field used as cover crop in sustainable agriculture.
Another agricultural field of red clover.

Traditional and Medicinal Uses
Historically, red clover featured in folk medicine for respiratory issues, skin conditions (eczema, psoriasis), and as a blood purifier. Today, it’s marketed as a dietary supplement for menopausal hot flashes, osteoporosis prevention, and cardiovascular health due to its phytoestrogens.
The flowers are brewed into teas or tinctures, while extracts are standardized for isoflavones.
Red clover herbal supplements in capsule form.
Another example of red clover extract capsules.
Phytochemical Composition and Health Benefits
Red clover is rich in isoflavones (biochanin A, formononetin, genistein, daidzein), which mimic estrogen and may alleviate menopausal symptoms. Other compounds include flavonoids, coumarins, and salicylates.
Studies suggest potential benefits for bone density, cholesterol reduction, and skin health, but results are mixed; it’s not recommended for hormone-sensitive conditions due to estrogenic effects.
Chemical structures of key isoflavones in red clover.
Ecological Role and Wildlife
As a nitrogen-fixer, red clover enhances biodiversity in pastures and attracts pollinators like bumblebees and honeybees. It’s a larval host for some butterflies and provides nectar for wildlife.
Safety and Side Effects
Generally safe in food amounts, but supplements may cause mild issues like rash or headache. Avoid in pregnancy, breastfeeding, or with blood thinners due to coumarin content. Consult healthcare providers for interactions.
Conclusion
Red clover bridges agriculture, ecology, and herbal medicine as a versatile legume. Its soil-improving properties support sustainable farming, while phytochemicals offer promising—though not fully proven—health applications. Whether in wild meadows or cultivated fields, red clover remains a valuable plant in natural and human systems.
More articles by ZMR Researche:
https://www.zionmarketresearch.com/de/report/liquid-crystal-polymers-lcps-market
https://www.zionmarketresearch.com/de/report/oncology-molecular-diagnostic-market
https://www.zionmarketresearch.com/de/report/hyaluronidase-market
https://www.zionmarketresearch.com/de/report/anticoagulant-reversal-drugs-market